Mint cDNA synthesis
Method overview
Mint cDNA synthesis is based on a novel technology (patent pending) utilizing the specific features of MMLV-based reverse transcriptase (RT). First strand cDNA synthesis starts from the 3'-primer comprising an oligo(dT) sequence to anneal to the polyA+ stretch of RNA. When RT reaches the 5' end of the mRNA, it adds several non-template nucleotides, primarily deoxycytidines, to the 3' end of the newly synthesized first-strand cDNA (Schmidt and Mueller, 1999). This oligo(dC) stretch base pairs to the complementary oligo(dG) sequence located at the 3' end of a special 30-mer deoxyribooligonucleotide called PlugOligo. RT identifies PlugOligo as an extra part of the RNA-template and continues first strand cDNA synthesis to the end of the oligonucleotide, thus incorporating PlugOligo sequence into the 5' end of cDNA.
The last 3'-dG residue of the PlugOligo is a terminator nucleotide comprising 3'-phosphate group. This blocking group prevents unwanted annealing and extension of the PlugOligo. Under standard conditions RT can hardly use PlugOligo as a template, however our special IP-solution (solution for Incorporation of PlugOligo sequence) dramatically increases the efficiency of this process. Synthesis of ds cDNA is then performed using PCR amplification.
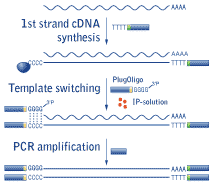 | Schematic outline of Mint cDNA synthesis. |
|---|
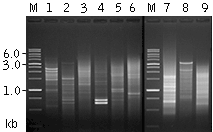 | Mint-amplified cDNA from different sources.1 - mouse liver; 2 - mouse skeletal muscle; 3 - mouse brain; 4 - human leucocytes; 5 - human lung; 6 - human skeletal muscle; 7 - mosquito grub; 8 - copepod Pontella sp.; 9 - tomato Lycopersicon esculentum. M - 1 kb DNA size marker, SibEnzyme, Russia. |
References:
- Schmidt WM, Mueller MW. CapSelect: a highly sensitive method for 5' CAP-dependent enrichment of full-length cDNA in PCR-mediated analysis of mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999; 27 (21):e31. / pmid: 10518626
